Raster data (with Rasters.jl)

Rasters.jl is a Julia package designed for working with raster data. It provides tools to read, write, and manipulate raster datasets, which are commonly used in geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, and similar fields where grid data is prevalent. It's built on top of DimensionalData.jl, which also underpins e.g. YAXArrays.jl.
In general, any input that works with base Makie will work with GeoMakie in a GeoAxis!
First, we'll load Rasters.jl, RasterDataSources.jl which provides access to common datasets, and ArchGDAL.jl which Rasters.jl depends on to read files.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDALWARNING: Method definition convert_arguments(MakieCore.CellGrid, Rasters.AbstractRaster{var"#s115", 2, D, A} where A where D where var"#s115") in module RastersMakieExt at /home/runner/.julia/packages/Rasters/PwNhf/ext/RastersMakieExt/plotrecipes.jl:304 overwritten at /home/runner/.julia/packages/Rasters/PwNhf/ext/RastersMakieExt/plotrecipes.jl:308.
ERROR: Method overwriting is not permitted during Module precompilation. Use `__precompile__(false)` to opt-out of precompilation.We'll also load GeoMakie and CairoMakie to plot the data.
using GeoMakie, CairoMakieFirst, we can load a Raster from the EarthEnv project, which represents habitat or ecosystem heterogeneity.
ras = Raster(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, :homogeneity) # habitat homogeneity to neighbouring pixel╭───────────────────────────────────────╮
│ 1728×696 Raster{UInt16,2} homogeneity │
├───────────────────────────────────────┴──────────────────────────────── dims ┐
↓ X Projected{Float64} LinRange{Float64}(-180.0, 179.79166666666669, 1728) ForwardOrdered Regular Intervals{Start},
→ Y Projected{Float64} LinRange{Float64}(84.79166666666667, -60.0, 696) ReverseOrdered Regular Intervals{Start}
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── metadata ┤
Metadata{Rasters.GDALsource} of Dict{String, Any} with 4 entries:
"units" => ""
"offset" => 0.0
"filepath" => "/home/runner/.julia/artifacts/EarthEnv/HabitatHeterogeneity/25…
"scale" => 1.0
├────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── raster ┤
extent: Extent(X = (-180.0, 180.00000000000003), Y = (-60.0, 85.0))
missingval: 0xffff
crs: GEOGCS["WGS 84",DATUM["WGS_1984",SPHEROID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY["EPSG","7030"]],AUTHORITY["EPSG","6326"]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]],UNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433,AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]],AXIS["Latitude",NORTH],AXIS["Longitude",EAST],AUTHORITY["EPSG","4326"]]
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓ → 84.7917 84.5833 … -59.5833 -59.7917 -60.0
-180.0 0xffff 0xffff 0xffff 0xffff 0xffff
⋮ ⋱ ⋮
179.792 0xffff 0xffff 0xffff 0xffff 0xffffLet's take a look at this in regular Makie first:
heatmap(ras; axis = (; aspect = DataAspect()))
We can plot this in any projection:
fig = Figure(); ga = GeoAxis(fig[1, 1])
hm = heatmap!(ga, ras)
fig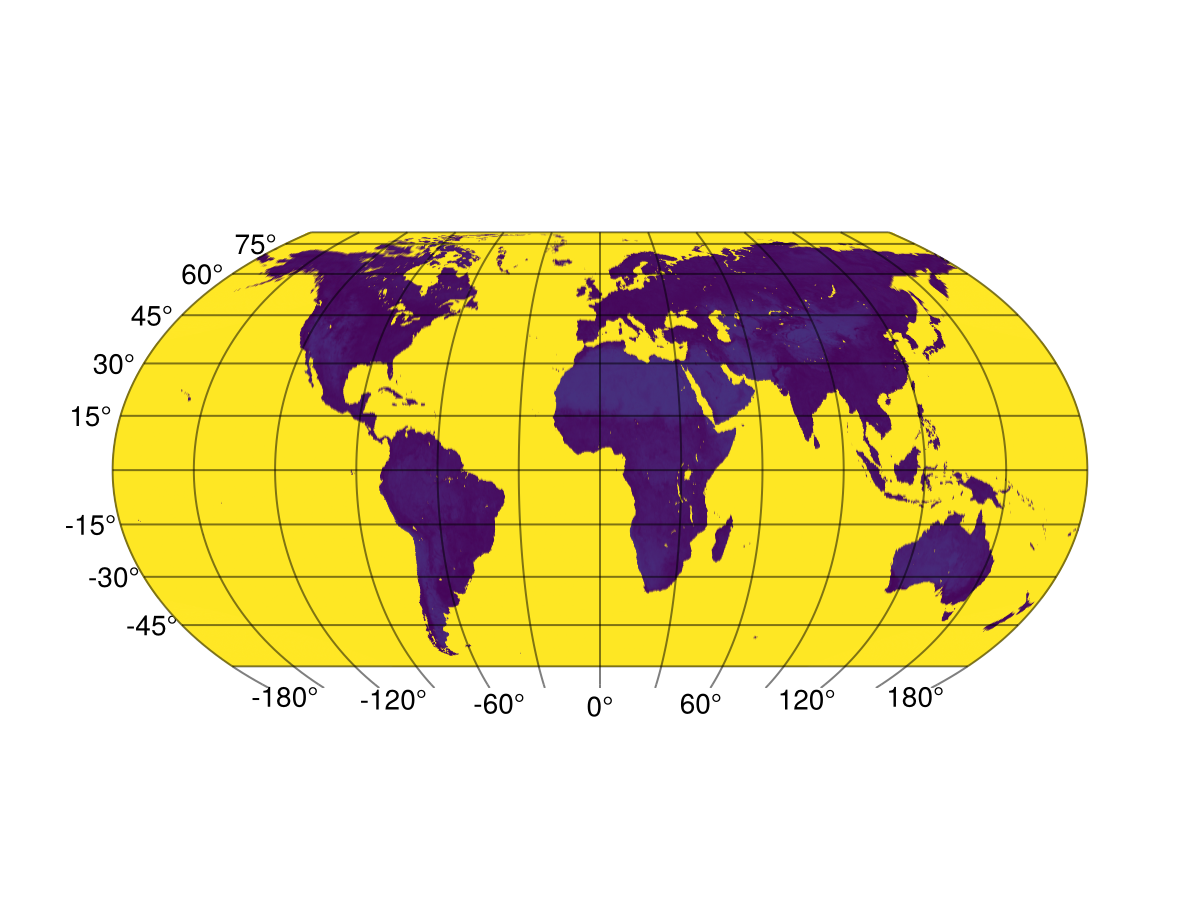
We can also change the projection arbitrarily:
ga.dest[] = "+proj=ortho +lon_0=19 +lat_0=72"
fig
and all other Makie keyword arguments also apply!
hm.colormap = :isoluminant_cgo_70_c39_n256
fig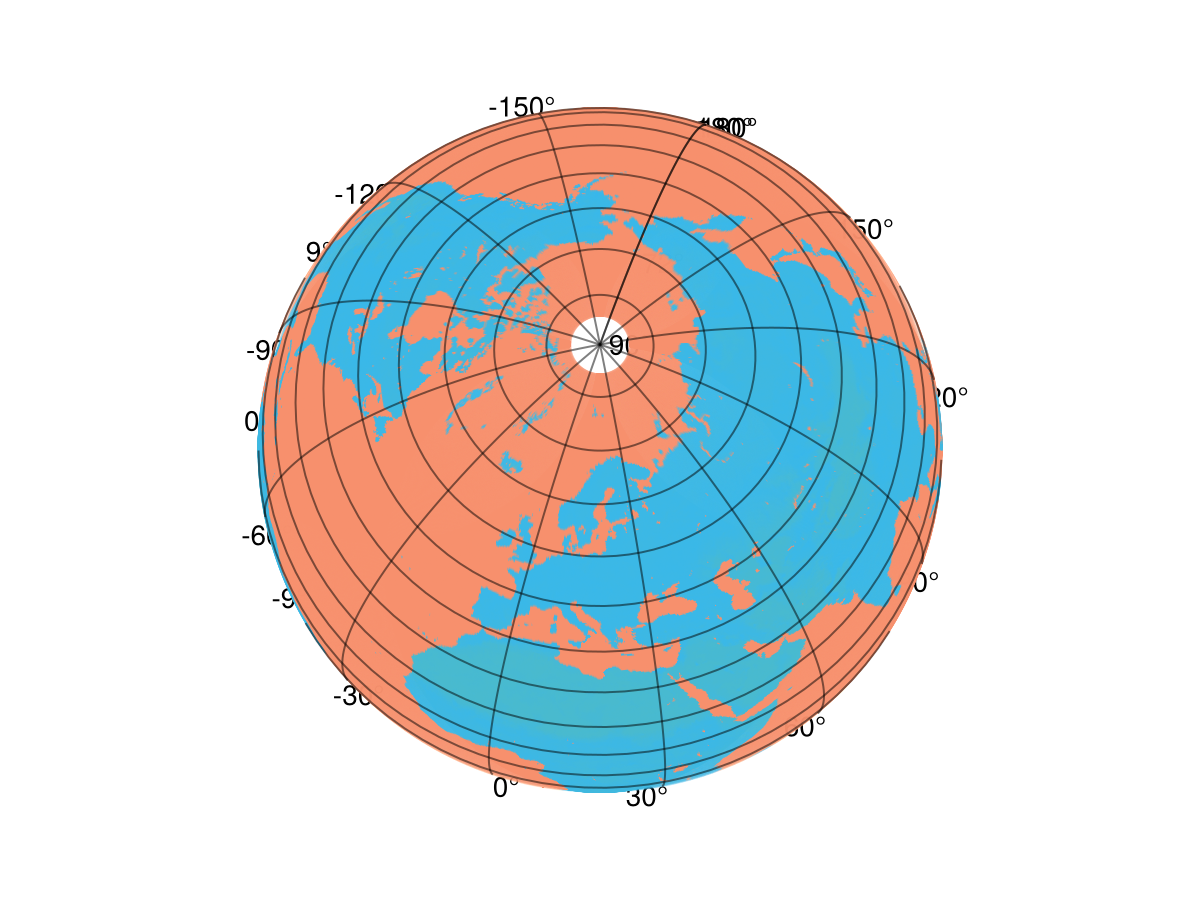
You can also use other recipes like surface:
fig = Figure(); ga = GeoAxis(fig[1, 1])
sp = surface!(ga, ras)
fig
This looks a bit strange - but you can always disable shading:
sp.shading = NoShading
fig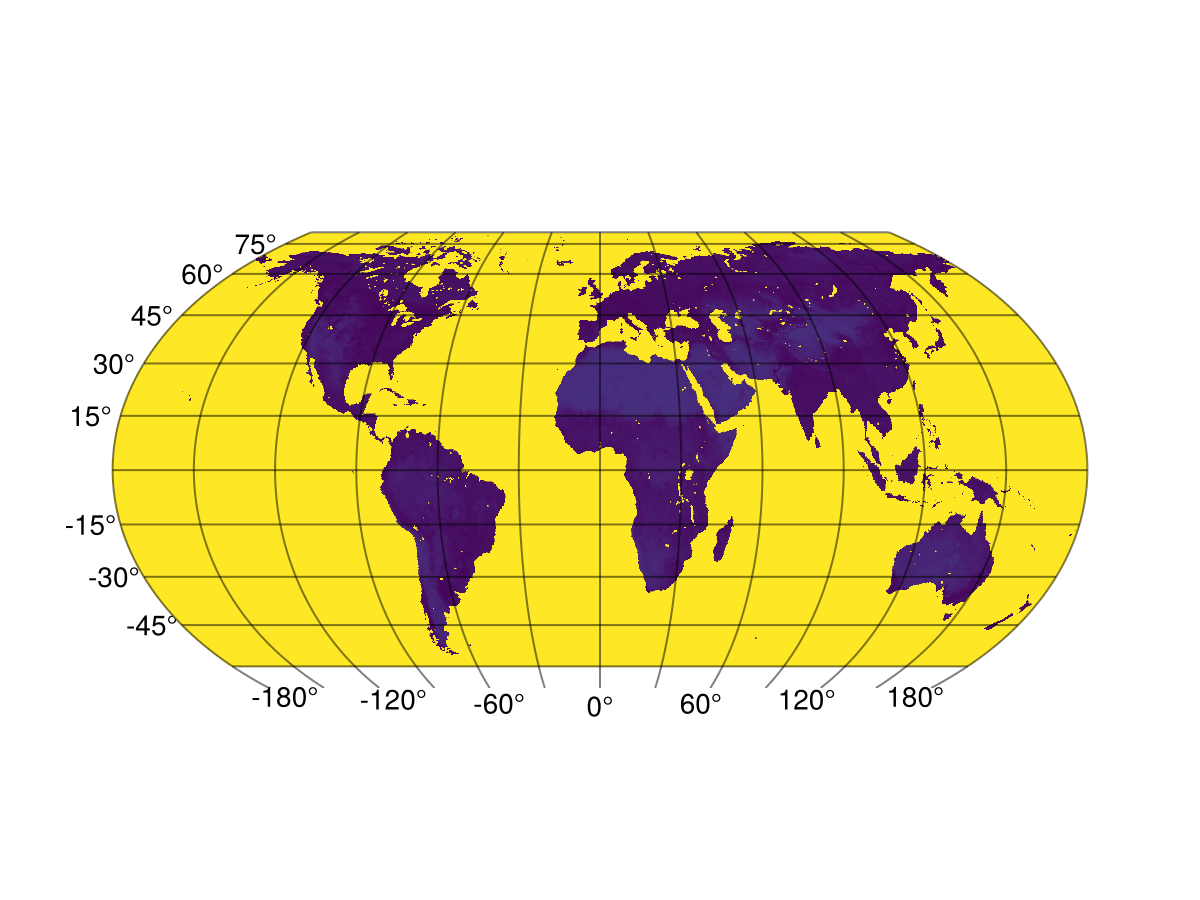
See also the Geostationary image and Multiple CRS examples, where we explore how to plot data in different projections.
This page was generated using Literate.jl.